What is Mocking ?
Mocking, in a broader software development and testing context, is a technique used to simulate the behavior of certain components or objects in a controlled manner. It involves creating fake or mock objects that imitate the behavior of real objects or components within a software system. Mocking is often used in various stages of software development, including testing, to isolate and focus on specific parts of a system while ignoring the complexities of its dependencies.
Mocking allows developers and testers to isolate specific parts of a system for testing without relying on the actual implementation of external components, services, or modules
Benefits of Mocking
Few of the befits of Mocking are
- Simulation of Dependencies: Mocking involves creating mock objects or functions that imitate the behavior of real components or services that a software system relies on. These mock objects or functions provide predefined responses to interactions, such as method calls or API requests.
- Isolation: Mocking helps in isolating the unit or component being tested from the rest of the system. This isolation ensures that any issues or failures detected during testing are specific to the unit under examination and not caused by external factors.
- Reduced Risk: Since mocking avoids the use of real external dependencies, there is a reduced risk of unintended side effects or data corruption during testing. The test environment remains controlled and predictable.
- Speed: Real dependencies might involve time-consuming operations or external services like databases, APIs, or network calls. Mocking these dependencies can significantly speed up the testing process because you eliminate the need to perform these real operations.
- Reduced Resource Usage: Since mocks don’t use real resources like databases or external services, they reduce the load on these resources during testing, which can be especially important in shared development and testing environments.
Mocking API In Cypress?
Mocking APIs in Cypress is a powerful technique for simulating APIs and external services in your tests. This allows you to create controlled environments for testing different scenarios without relying on the actual services.To mock an API in Cypress, you can use the cy.intercept() command. This command intercepts HTTP requests and returns a predefined response.
Cypress’s cy.intercept() method empowers developers and testers to intercept and manipulate network requests, allowing them to simulate various scenarios and responses, thus making it an indispensable tool for testing in dynamic and unpredictable environments. By crafting custom responses or simulating error conditions, you can comprehensively assess your application’s behavior under diverse conditions.
To use cy.intercept(), you must first specify the method and url of the request to intercept. You can also specify other parameters, such as the request body and headers. The second argument to cy.intercept() is the response that you want to return.
For example, the following code mocks the response to a GET request to the /api/users endpoint:
cy.intercept('GET', '/api/users', {
statusCode: 200,
body: [
{
id: 1,
name: 'John Doe',
email: '[email protected]',
},
{
id: 2,
name: 'Jane Doe',
email: '[email protected]',
},
],
});
Example Mocking API Data In Cypress
Step 1 Create Scenario For To Automate
To gain deeper insights, we’ll automate a specific scenario on https://demo.realworld.io/.
Below steps we are going to automate for Mocking the data :
- Visit the website at https://demo.realworld.io/.
- Upon opening the page, two requests are triggered in Network call — one for Tags and other for Article
- Intercept the Tags request, and instead of the original list of Tags, insert three new tags: “Cypress”“Playwright” and “SLASSCOM” Make sure to verify that these tags are displayed correctly in the user interface.
- Intercept the Article request, and instead of the original list of articles, provide just one article with modified details. You should change the username, description, and the number of likes. Afterward, confirm that these modifications are accurately reflected in the user interface.
tags:
Feeds
Before Automating the above steps lets create the data that we want to Mock
Step 2 Create Data To Mock the API
Create two file with name mockTags.json, mockArticles.json
mockTags.json
{
"tags":[
"Cypress",
"Playwright",
"SLASSCOM"
]
}
mockArticles.json
{
"articles":[
{
"title":"Hi qaautomationlabs.com",
"slug":"Hi - qaautomationlabs.com",
"body":"qaautomationlabs",
"createdAt":"2020-09-26T03:18:26.635Z",
"updatedAt":"2020-09-26T03:18:26.635Z",
"tagList":[
],
"description":"SLASSCOM QUALITY SUMMIT 2023",
"author":{
"username":"Kailash Pathak",
"bio":null,
"image":"https://static.productionready.io/images/smiley-cyrus.jpg",
"following":false
},
"favorited":false,
"favoritesCount":1000
}
],
"articlesCount":500
}
Step 3 Create Script
Let’s create Script for mocking the API data:
describe("API Mocking in Cypress using cy.intercept Method ", () => {
beforeEach(() => {
cy.visit("https://demo.realworld.io/");
cy.intercept("GET", "https://api.realworld.io/api/tags", {
fixture: "mockTags.json",
});
cy.intercept(
"GET",
"https://api.realworld.io/api/articles?limit=10&offset=0",
{ fixture: "mockArticles.json" }
);
});
it("Mock API Tags, and then validate on UI", () => {
cy.get(".tag-list", { timeout: 1000 })
.should("contain", "Cypress")
.and("contain", "Playwright");
});
it("Mock the Article feed, and then validate on UI", () => {
cy.get("app-favorite-button.pull-xs-right").contains("10");
cy.get(".author").contains("Kailash Pathak");
cy.get(".preview-link > p").contains("SLASSCOM QUALITY SUMMIT 2023");
});
});
Code walkthrough
Below the detail explanation of the above code step by step:
describe("API Mocking in Cypress using cy.intercept Method", () => { ... }): This is a test suite description. It defines a test suite titled “API Mocking in Cypress using cy.intercept Method.”beforeEach(() => { ... }): This is a hook that runs before each test case in the suite. It sets up the initial conditions for the tests.cy.visit("https://angular.realworld.io/");: It opens a web page at the URL “https://demo.realworld.io/” using Cypress.cy.intercept("GET", "https://api.realworld.io/api/tags", { fixture: "mockTags.json" });: This line intercepts a GET request to “https://api.realworld.io/api/tags” and responds with data from the fixture file “mockTags.json.” It mocks the API call to retrieve tags.cy.intercept("GET", "https://api.realworld.io/api/articles?limit=10&offset=0", { fixture: "mockArticles.json" });: Similar to the previous line, this intercepts a GET request to “https://api.realworld.io/api/articles?limit=10&offset=0” and responds with data from the fixture file “mockArticles.json.” It mocks the API call to retrieve articles.it("Mock API Tags, and then validate on UI", () => { ... }): This is the first test case. It verifies that the mocked tags are displayed on the UI.cy.get(".tag-list", { timeout: 1000 })...: It selects an element with the class “tag-list” and waits for it to appear for up to 1000 milliseconds. Then, it checks if it contains the tags “Cypress” and “Playwright.”it("Mock the Article feed, and then validate on UI", () => { ... }): This is the second test case. It verifies that the mocked articles are displayed correctly on the UI.cy.get("app-favorite-button.pull-xs-right").contains("10");: It selects an element with the class “app-favorite-button.pull-xs-right” and checks if it contains the text “10.”cy.get(".author").contains("Kailash Pathak");: It selects an element with the class “author” and checks if it contains the text “Kailash Pathak.”cy.get(".preview-link > p").contains("SLASSCOM QUALITY SUMMIT 2023");: It selects an element with the class “preview-link” and checks if it contains the text “SLASSCOM QUALITY SUMMIT 2023.”
Step 4 Execute the Script
Run the command ‘yarn Cypress Open'
Default Data displaying in the site :
Below tags are displaying by default in the site

Below Feed are displaying by default in the site

Data After Mocking the data
In below screenshot you can see that the data that we have provided in mockTags.json (i.e Cypress Playwright,SLASSCOM) replace the existing default tags
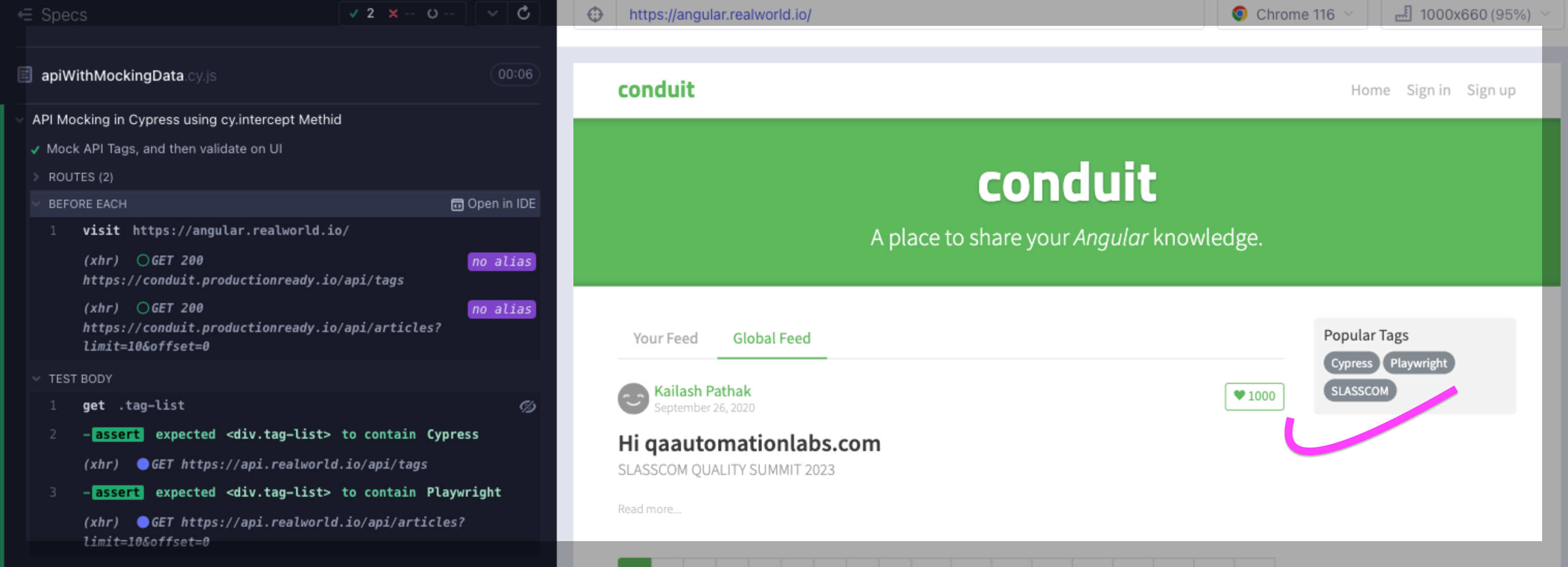
In below screenshot you can see that the data that we have provided in mockArticles.json (i.e username,description and favorites count) replace existing default Feeds

Conclusion
In conclusion, mocking API responses in Cypress is a powerful technique for testing your application’s frontend behavior in a controlled and predictable manner. It promotes faster, more reliable, and isolated testing of various scenarios, helping you catch bugs and ensure your application works as intended. Properly maintained mock data and well-structured tests can be invaluable assets in your testing strategy.’
